UND MATHEMATICS TRACK MEET Individual Test 2
University of North Dakota Grades 11/12
January 12, 2026
School Team Name
Calculators are NOT allowed. Solutions Student Name
-
1.
Let be a function satisfying
and is a natural number for all natural numbers . Find .
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(2 pts) 1. (c)
Solution: Since is an increasing function, we must have for all . Indeed, suppose on the contrary that for some , we have
which is a contradiction. Putting , we must have for all , which deduces that
Combining this with the assumption, we have
In other words,
which implies that for all . Since is a natural number, we must have for all . This means that for all So
-
2.
For how many integers is a perfect square?
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) infinitely many
(3 pts) 2. (a)
Solution: We want such that is a perfect square. Rewrite
Let , so
The integer factor pairs of are , , , . Solving from , , each gives either a noninteger or . Thus no works. Therefore the answer is .
-
3.
Let be a nonzero polynomial satisfying
for all real numbers Which is the degree of
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(3 pts) 3. (e)
Solution: We can rewrite the above equation as
() Choose we deduce that Choose , we deduce that Choose , we deduce from the above equation and that . Choose , we deduce from the above equation and that Therefore, we can find a polynomial such that
which implies from () that
or
which implies that for all , where This means that must be a constant . Thus, which implies that
Hence, the degree of is
-
4.
Two triangles have the same perimeter. The first has side ratios and the second has ratios . What is the ratio of their areas?
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(3 pts) 4. (c)
Solution: Let the similar triangles have scale factors and , so their sides are and . Equal perimeters give
Both triangles are right triangles, so their areas are
Thus
Therefore, the ratio of their areas is .
-
5.
Triangle has area . A point moves along side . Through , draw a line parallel to meeting at , and a line parallel to meeting at . The quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Find the maximum possible area of parallelogram .
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(3 pts) 5. (c)
Solution:
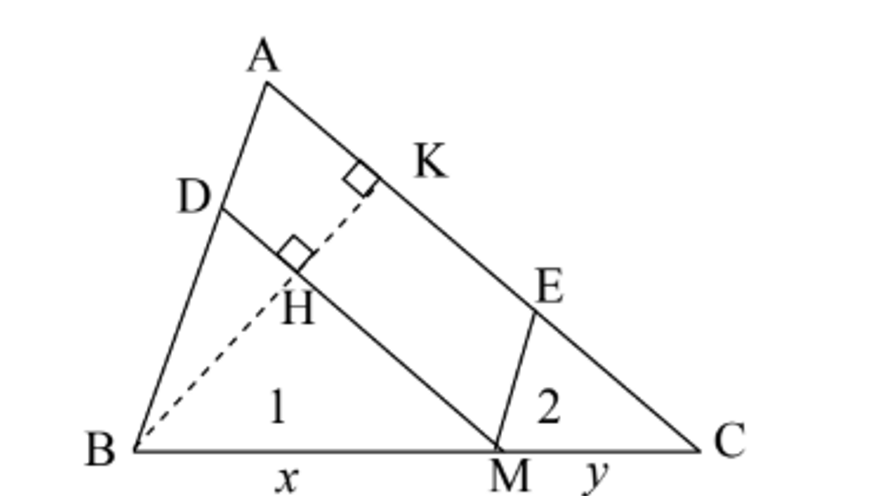
Maximizing is equivalent to maximizing the ratio
Draw intersecting at . Then
so
Let and . Since , we have
By the inequality
Equality occurs when . Therefore,
which happens when is the midpoint of .
-
6.
A teacher has 300 identical books and wants to pack them into boxes with a different number of books in each box. What is the greatest possible number of boxes?
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) none of these
(3 pts) 6. (b)
Solution: Suppose the boxes have sizes . Then the total number of books is
We require This inequality is equivalent to The positive root of the quadratic equation is Thus . Since
the value is achievable. For , we would need
which is impossible. Therefore, the greatest possible number of boxes is .
-
7.
How many pairs of integers satisfy the equation ?
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) no integer is satisfied
(3 pts) 7. (b)
Solution: We want integers such that
Cross–multiply:
Let and . Then , so
For integer solutions, we need an integer and the discriminant
to be a nonnegative perfect square. Substitute :
Thus is an integer only if , so write . Then
For we need or . The case gives , which is not allowed since . Thus , giving and .
Therefore
The integer solutions are and , so the answer is .
