Chapter 11
Exercises 11.1
-
1.
right hand
-
3.
curve (a parabola); surface (a cylinder)
-
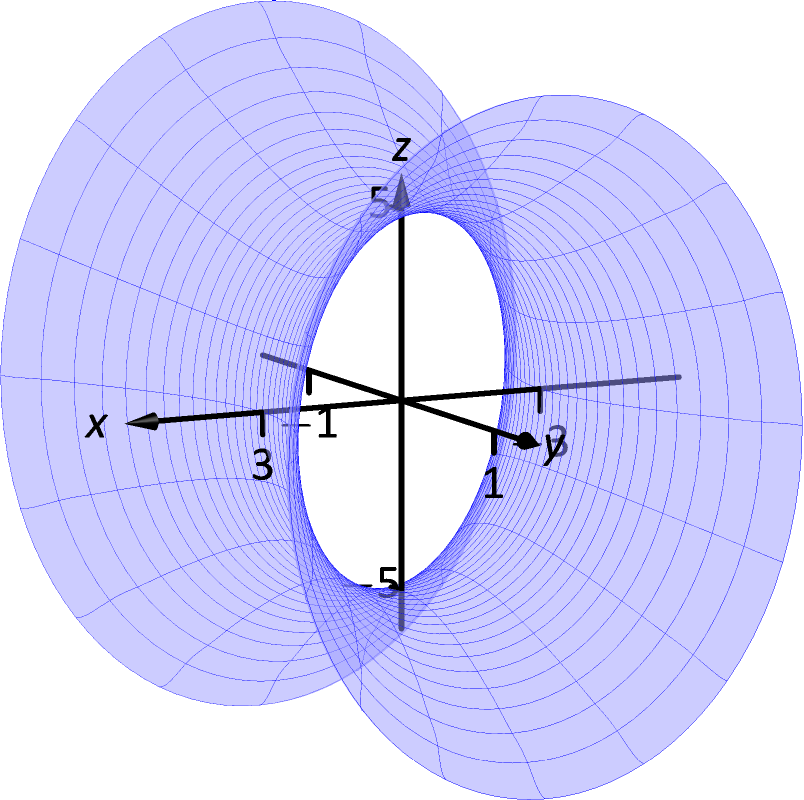
5.
a hyperboloid of two sheets
-
7.
; ; . Yes, it is a right triangle as .
- 9.
-
11.
, , . The points do not lie on a line.
-
13.
Center at ; radius = 3
-
15.
closer to the surface
-
17.
Interior of a sphere with radius 1 centered at the origin.
-
19.
The first octant of space along with its adjacent quarter planes; all points where each of , and are positive or zero. (Analogous to the first quadrant in the plane.)
-
21.
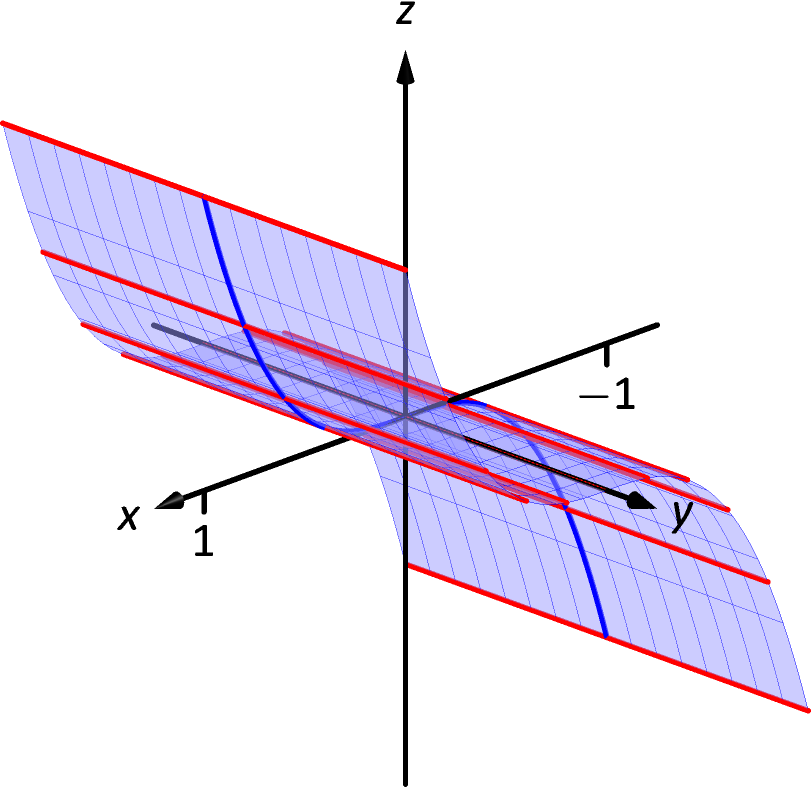
-
23.
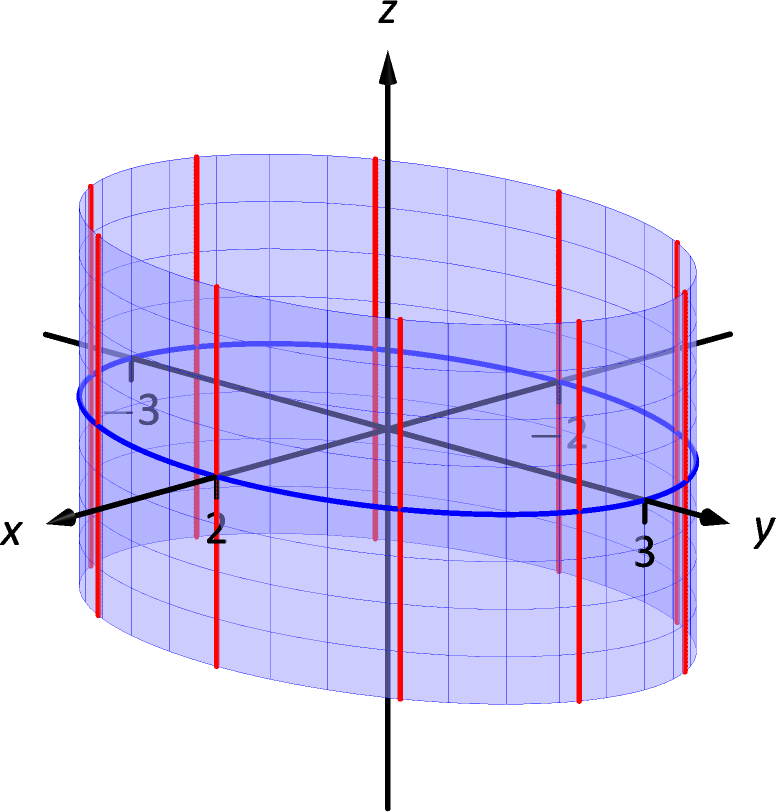
-
25.
-
27.
-
29.
(a)
-
31.
(b)
-
33.
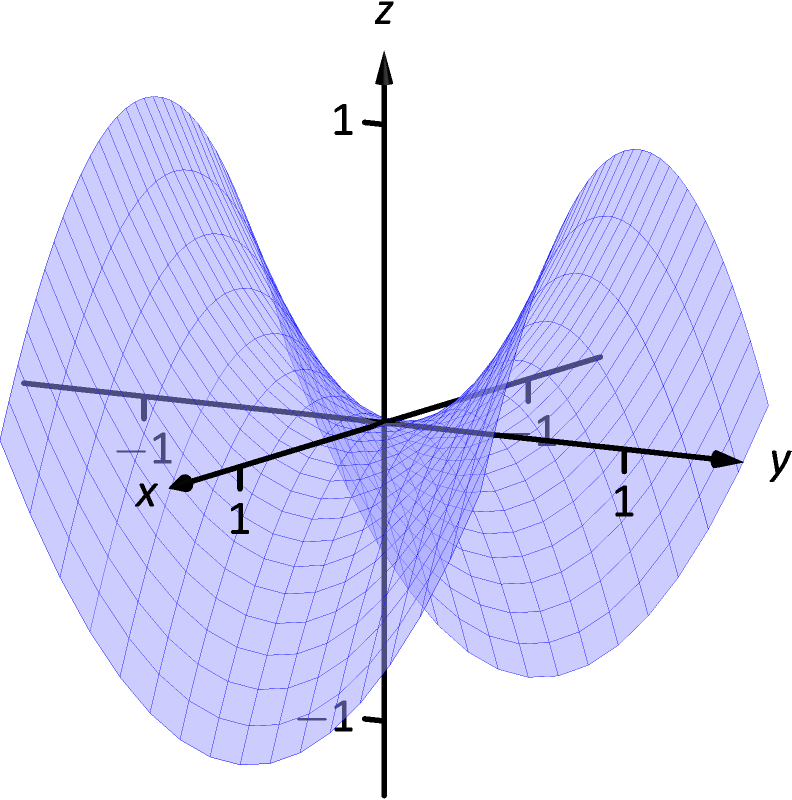
-
35.
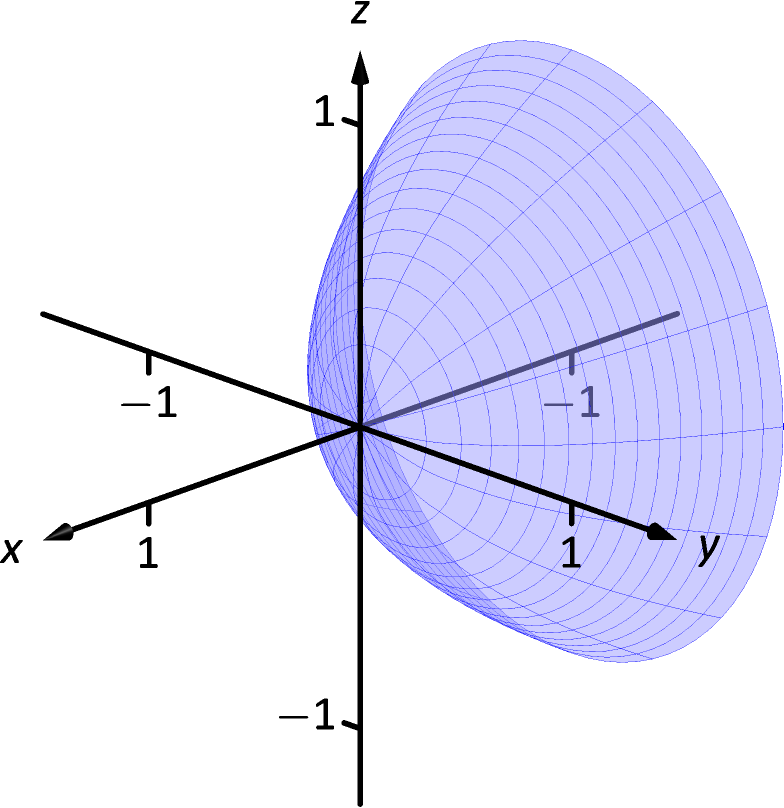
-
37.
- 39.
Exercises 11.2
-
1.
Answers will vary.
-
3.
A vector with magnitude 1.
-
5.
Their respective unit vectors are parallel; unit vectors and are parallel if .
-
7.
-
9.
-
11.
(a) ; ; . (c) .
-
13.
-
15.
-
17.
, , ,
-
19.
, , ,
-
21.
-
23.
-
25.
When and have the same direction. (Note: parallel is not enough.)
-
27.
.
-
29.
The magnitude of the force on each chain is lb.
-
31.
The magnitude of the force on the chain with angle is approx. lb; the magnitude of the force on the chain with angle is approx. lb.
-
33.
; the weight is lifted ft (about 3.5in).
-
35.
; the weight is lifted ft.
- 37.
- 39.
Exercises 11.3
-
1.
Scalar
-
3.
By considering the sign of the dot product of the two vectors. If the dot product is positive, the angle is acute; if the dot product is negative, the angle is obtuse.
-
5.
-
7.
-
9.
not defined
-
11.
Answers will vary.
-
13.
-
15.
-
17.
Answers will vary; two possible answers are and .
-
19.
Answers will vary; two possible answers are and .
-
21.
.
-
23.
.
-
25.
.
-
27.
.
-
29.
.
-
31.
.
-
33.
1.96lb
-
35.
ft-lb
-
37.
ft-lb
-
39.
ft-lb
- 41.
- 43.
- 45.
Exercises 11.4
-
1.
vector
-
3.
“Perpendicular” is one answer.
-
5.
Torque
-
7.
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
-
9.
18
-
11.
0
-
13.
-
15.
-
17.
-
19.
-
21.
Answers will vary.
-
23.
5
-
25.
0
-
27.
-
29.
-
31.
-
33.
-
35.
-
37.
-
39.
-
41.
-
43.
ft-lb
-
45.
ft-lb
-
47.
With and , we have
- 49.
- 51.
- 53.
- 55.
- 57.
- 59.
Exercises 11.5
-
1.
A point on the line and the direction of the line.
-
3.
parallel, skew
-
5.
vector: parametric: , , symmetric:
-
7.
Answers can vary: vector: parametric: , , symmetric:
-
9.
Answers can vary; here the direction is given by : vector: parametric: , , symmetric:
-
11.
Answers can vary; here the direction is given by : vector: parametric: , , symmetric:
-
13.
vector: parametric: , symmetric:
-
15.
parallel
-
17.
intersecting;
-
19.
skew
-
21.
same
-
23.
-
25.
-
27.
-
29.
Since both and are on the line, is parallel to . Thus , giving a distance of .
-
31.
(a) The distance formula cannot be used because since and are parallel, is and we cannot divide by . (b) Since and are parallel, lies in the plane formed by the two lines. Thus is orthogonal to this plane, and is parallel to the plane, but still orthogonal to both and . We desire the length of the projection of onto , which is what the formula provides. (c) Since the lines are parallel, one can measure the distance between the lines at any location on either line (just as to find the distance between straight railroad tracks, one can use a measuring tape anywhere along the track, not just at one specific place.) Let and as given by the equations of the lines, and apply the formula for distance between a point and a line.
Exercises 11.6
-
1.
A point in the plane and a normal vector (i.e., a direction orthogonal to the plane).
-
3.
Answers will vary.
-
5.
Answers will vary.
-
7.
Standard form: general form:
-
9.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
11.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
13.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
15.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
17.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
19.
Answers may vary; Standard form: general form:
-
21.
Answers may vary:
-
23.
-
25.
No point of intersection; the plane and line are parallel.
-
27.
-
29.
-
31.
If is any point in the plane, and is also in the plane, then lies parallel to the plane and is orthogonal to , the normal vector. Thus , giving the distance as 0.
