12.2 Calculus and Vector-Valued Functions
The previous section introduced us to a new mathematical object, the vector-valued function. We now apply calculus concepts to these functions. We start with the limit, then work our way through derivatives to integrals.
Limits of Vector-Valued Functions
The initial definition of the limit of a vector-valued function is a bit intimidating, as was the definition of the limit in Definition 1.2.1. The theorem following the definition shows that in practice, taking limits of vector-valued functions is no more difficult than taking limits of real-valued functions.
Definition 12.2.1 Limits of Vector-Valued Functions
Let be an open interval containing , and let be a vector-valued function defined on , except possibly at . The limit of , as approaches , is , expressed as
means that given any , there exists a such that for all , if , we have
Note how the measurement of distance between real numbers is the absolute value of their difference; the measure of distance between vectors is the vector norm, or magnitude, of their difference.
Theorem 12.2.1 Limits of Vector-Valued Functions
-
1.
Let be a vector-valued function in defined on an open interval containing . Then
-
2.
Let be a vector-valued function in defined on an open interval containing . Then
If any of the component limits do not exist, then does not exist.
Theorem 12.2.1 states that we compute limits component-wise.
Example 12.2.1 Finding limits of vector-valued functions
Let Find .
SolutionWe apply the theorem and compute limits component-wise.
Continuity
Definition 12.2.2 Continuity of Vector-Valued Functions
Let be a vector-valued function defined on an open interval containing .
-
1.
is continuous at if .
-
2.
If is continuous at all in , then is continuous on .
We again have a theorem that lets us evaluate continuity component-wise.
Theorem 12.2.2 Continuity of Vector-Valued Functions
Let be a vector-valued function defined on an open interval containing . Then is continuous at if, and only if, each of its component functions is continuous at .
Example 12.2.2 Evaluating continuity of vector-valued functions
Let Determine whether is continuous at and .
SolutionWhile the second and third components of are defined at , the first component, , is not. Since the first component is not even defined at , is not defined at , and hence it is not continuous at .
At each of the component functions is continuous. Therefore is continuous at .
Derivatives
Consider a vector-valued function defined on an open interval containing and . We can compute the displacement of on , as shown in Figure 12.2.1(a). Recall that dividing the displacement vector by gives the average rate of change on , as shown in (b).
The derivative of a vector-valued function is a measure of the instantaneous rate of change, measured by taking the limit as the length of goes to 0. Instead of thinking of an interval as , we think of it as for some value of (hence the interval has length ). The average rate of change is
for any value of . We take the limit as to measure the instantaneous rate of change; this is the derivative of .
Definition 12.2.3 Derivative of a Vector-Valued Function
Let be continuous on an open interval containing .
-
1.
The derivative of at is
-
2.
The derivative of is
If a vector-valued function has a derivative for all in an open interval , we say that is differentiable on .
Once again we might view this definition as intimidating, but recall that we can evaluate limits component-wise. The following theorem verifies that this means we can compute derivatives component-wise as well, making the task not too difficult.
Theorem 12.2.3 Derivatives of Vector-Valued Functions
-
1.
Let . Then
-
2.
Let . Then
If any of the component derivatives do not exist, then does not exist.
Example 12.2.3 Derivatives of vector-valued functions
Let .
-
1.
Sketch and on the same axes.
-
2.
Compute and sketch this vector with its initial point at the origin and at .
Solution
-
1.
Theorem 12.2.3 allows us to compute derivatives component-wise, so
and are graphed together in Figure 12.2.2(a). Note how plotting the two of these together, in this way, is not very illuminating. When dealing with real-valued functions, plotting with gave us useful information as we were able to compare and at the same -values. When dealing with vector-valued functions, it is hard to tell which points on the graph of correspond to which points on the graph of .
-
2.
We easily compute , which is drawn in Figure 12.2.2 with its initial point at the origin, as well as at These are sketched in Figure 12.2.2(b).
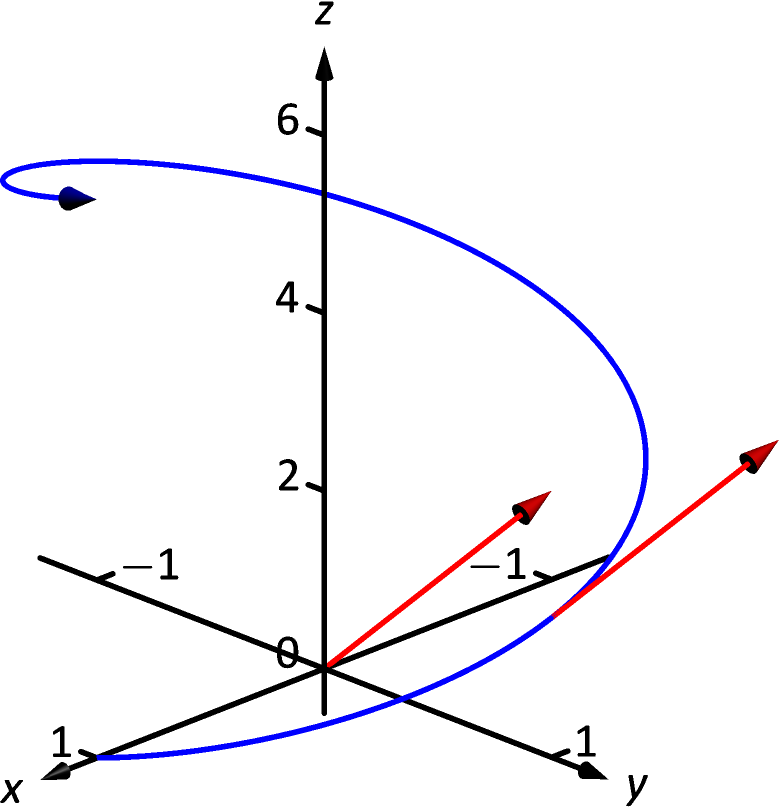 Figure 12.2.3: Viewing a vector-valued function and its derivative at one point.
Figure 12.2.3: Viewing a vector-valued function and its derivative at one point.
Example 12.2.4 Derivatives of vector-valued functions
Let . Compute and . Sketch with its initial point at the origin and at .
SolutionWe compute as . At , we have . Figure 12.2.3 shows a graph of , with plotted with its initial point at the origin and at .
In Examples 12.2.3 and 12.2.4, sketching a particular derivative with its initial point at the origin did not seem to reveal anything significant. However, when we sketched the vector with its initial point on the corresponding point on the graph, we did see something significant: the vector appeared to be tangent to the graph. We have not yet defined what “tangent” means in terms of curves in space; in fact, we use the derivative to define this term.
Definition 12.2.4 Tangent Vector, Tangent Line
Let be a differentiable vector-valued function on an open interval containing , where .
-
1.
A vector is tangent to the graph of at if is parallel to .
-
2.
The tangent line to the graph of at is the line through with direction parallel to . An equation of the tangent line is
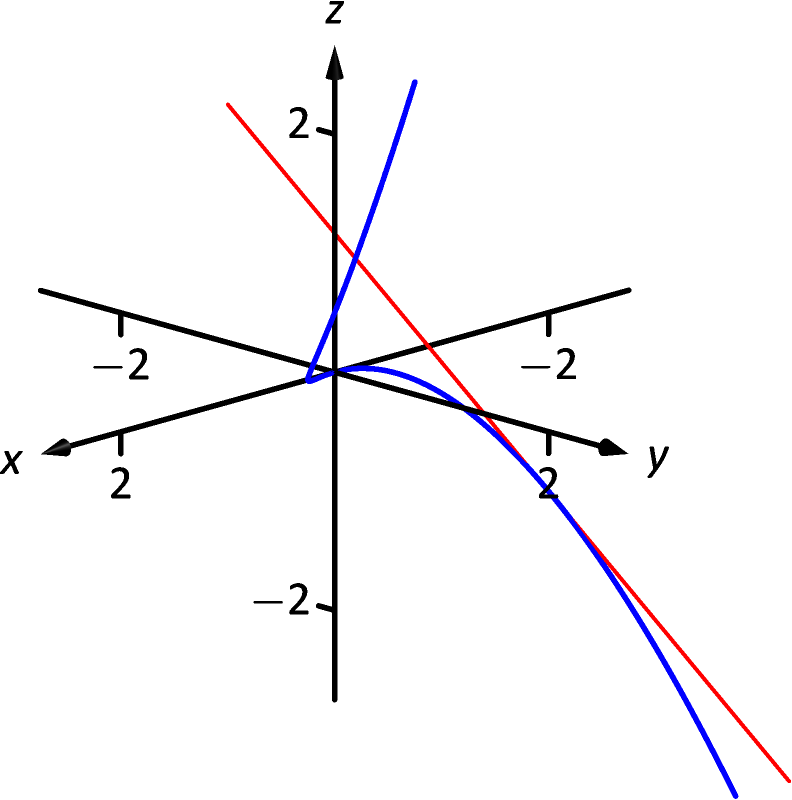 Figure 12.2.4: Graphing a curve in space with its tangent line.
Figure 12.2.4: Graphing a curve in space with its tangent line.
Example 12.2.5 Finding tangent lines to curves in space
Let on . Find the vector equation of the line tangent to the graph of at .
SolutionTo find the equation of a line, we need a point on the line and the line’s direction. The point is given by . (To be clear, is a vector, not a point, but we use the point “pointed to” by this vector.)
The direction comes from . We compute, component-wise, . Thus .
The vector equation of the line is . This line and are sketched in Figure 12.2.4.
Example 12.2.6 Finding tangent lines to curves
Find the equations of the lines tangent to at and .
SolutionWe find that . At , we have
so the equation of the line tangent to the graph of at is
This line is graphed with in Figure 12.2.5.
At , we have . This implies that the tangent line “has no direction.” We cannot apply Definition 12.2.4, hence cannot find the equation of the tangent line.
We were unable to compute the equation of the tangent line to at because . The graph in Figure 12.2.5 shows that there is a cusp at this point. This leads us to another definition of smooth, previously defined by Definition 10.2.2 in Section 10.2.
Definition 12.2.5 Smooth Vector-Valued Functions
Let be a differentiable vector-valued function on an open interval . Then is smooth on if is continuous and on .
Having established derivatives of vector-valued functions, we now explore the relationships between the derivative and other vector operations. The following theorem states how the derivative interacts with vector addition and the various vector products.
Theorem 12.2.4 Properties of Derivatives of Vector-Valued Functions
Let and be differentiable vector-valued functions, let be a differentiable real-valued function, and let be a real number.
-
1.
-
2.
-
3.
Product Rule
-
4.
Product Rule
-
5.
Product Rule
-
6.
Chain Rule
Example 12.2.7 Using derivative properties of vector-valued functions
Let and let be the unit vector that points in the direction of .
-
1.
Graph and on the same axes, on .
-
2.
Find and sketch , and . Sketch each with initial point the corresponding point on the graph of .
Solution
-
1.
To form the unit vector that points in the direction of , we need to divide by its magnitude.
††margin: Figure 12.2.6: Graphing and in Example 12.2.7.and are graphed in Figure 12.2.6. Note how the graph of forms part of a circle; this must be the case, as the length of is 1 for all .
-
2.
To compute , we use Theorem 12.2.4, writing
(We could write
and then take the derivative. It is a matter of preference; this latter method requires two applications of the Quotient Rule where our method uses the Product and Chain Rules.)
We find using the Chain Rule:
We now find using part 3 of Theorem 12.2.4:
This is admittedly very “messy;” such is usually the case when we deal with unit vectors. We can use this formula to compute , and :
††margin: Figure 12.2.7: Graphing some of the derivatives of in Example 12.2.7.Each of these is sketched in Figure 12.2.7. Note how the length of the vector gives an indication of how quickly the circle is being traced at that point. When , the circle is being drawn relatively slow; when , the circle is being traced much more quickly.
It is a basic geometric fact that a line tangent to a circle at a point is perpendicular to the line passing through the center of the circle and . This is illustrated in Figure 12.2.7; each tangent vector is perpendicular to the line that passes through its initial point and the center of the circle. Since the center of the circle is the origin, we can state this another way: is orthogonal to .
Recall that the dot product serves as a test for orthogonality: if , then is orthogonal to . Thus in the above example, .
This is true of any vector-valued function that has a constant length, that is, that traces out part of a circle. It has important implications later on, so we state it as a theorem (and leave its formal proof as Exercise 47.)
Theorem 12.2.5 Vector-Valued Functions of Constant Length
Let be a differentiable vector-valued function on an open interval of constant length. That is, for all in (equivalently, for all in ). Then for all in .
Integration
Indefinite and definite integrals of vector-valued functions are also defined to be evaluated component-wise.
Definition 12.2.6 Indefinite and Definite Integrals of Vector-Valued Functions
Let be a vector-valued function in .
-
1.
-
2.
Let be a vector-valued function in .
-
1.
-
2.
Example 12.2.8 Evaluating a definite integral of a vector-valued function
Let . Evaluate .
SolutionWe follow Definition 12.2.6.
Example 12.2.9 Solving an initial value problem
Let . Find where:
-
•
and
-
•
SolutionKnowing , we find by evaluating the indefinite integral.
Note how each indefinite integral creates its own constant which we collect as one constant vector . Knowing allows us to solve for :
So . To find , we integrate once more.
With , we solve for :
Therefore,
What does the integration of a vector-valued function mean? There are many applications, but none as direct as “the area under the curve” that we used in understanding the integral of a real-valued function.
A key understanding for us comes from considering the integral of a derivative:
Integrating a rate of change function gives displacement.
Noting that vector-valued functions are closely related to parametric equations, we can describe the arc length of the graph of a vector-valued function as an integral. Given parametric equations , , the arc length on of the graph is
as stated in Theorem 10.3.1 in Section 10.3. If , note that . Therefore we can express the arc length of the graph of a vector-valued function as an integral of the magnitude of its derivative.
Theorem 12.2.6 Arc Length of a Vector-Valued Function
Let be a vector-valued function where is continuous on . The arc length of the graph of is
Note that we are actually integrating a scalar-function here, not a vector-valued function.
The next section takes what we have established thus far and applies it to objects in motion. We will let describe the path of an object in the plane or in space and will discover the information provided by and .
Exercises 12.2
Terms and Concepts
-
1.
Limits, derivatives and integrals of vector-valued functions are all evaluated -wise.
-
2.
The definite integral of a rate of change function gives .
-
3.
Why is it generally not useful to graph both and on the same axes?
-
4.
Theorem 12.2.4 contains three product rules. What are the three different types of products used in these rules?
Problems
In Exercises 5–8, evaluate the given limit.
-
5.
-
6.
-
7.
-
8.
, where .
In Exercises 9–10, identify the interval(s) on which is continuous.
-
9.
-
10.
In Exercises 11–16, find the derivative of the given function.
-
11.
-
12.
-
13.
-
14.
-
15.
-
16.
In Exercises 17–20, find . Sketch and , with the initial point of at .
-
17.
-
18.
-
19.
-
20.
In Exercises 21–24, give the equation of the line tangent to the graph of at the given value.
-
21.
at .
-
22.
at .
-
23.
at .
-
24.
at .
In Exercises 25–28, find the value(s) of for which is not smooth.
-
25.
-
26.
-
27.
-
28.
Exercises 29–32 ask you to verify parts of Theorem 12.2.4. In each let , and . Compute the various derivatives as indicated.
-
29.
Simplify , then find its derivative; show this is the same as .
-
30.
Simplify , then find its derivative; show this is the same as .
-
31.
Simplify , then find its derivative; show this is the same as .
-
32.
Simplify , then find its derivative; show this is the same as .
In Exercises 33–36, evaluate the given definite or indefinite integral.
-
33.
-
34.
-
35.
-
36.
In Exercises 37–40, solve the given initial value problems.
-
37.
Find , given that and .
-
38.
Find , given that and .
-
39.
Find , given that , and .
-
40.
Find , given that , and .
In Exercises 41–46, find the arc length of on the indicated interval.
-
41.
on .
-
42.
on .
-
43.
on .
-
44.
on .
-
45.
on .
-
46.
on .
-
47.
Prove Theorem 12.2.5; that is, show if has constant length and is differentiable, then . (Hint: use the Product Rule to compute .)
-
48.
The graph of for is a helix of radius which completes turns and has height . Find the length of this curve.
